IEEE CVPR 2021 (Oral)
Deep Implicit Templates for 3D Shape Representation
Zerong Zheng, Tao Yu, Qionghai Dai, Yebin Liu
Tsinghua University
Abstract
Deep implicit functions (DIFs), as a kind of 3D shape representation, are becoming more and more popular in the 3D vision community due to their compactness and strong representation power. However, unlike polygon mesh-based templates, it remains a challenge to reason dense correspondences or other semantic relationships across shapes represented by DIFs, which limits its applications in texture transfer, shape analysis and so on. To overcome this limitation and also make DIFs more interpretable, we propose Deep Implicit Templates, a new 3D shape representation that supports explicit correspondence reasoning in deep implicit representations. Our key idea is to formulate DIFs as conditional deformations of a template implicit function. To this end, we propose Spatial Warping LSTM, which decomposes the conditional spatial transformation into multiple affine transformations and guarantees generalization capability. Moreover, the training loss is carefully designed in order to achieve high reconstruction accuracy while learning a plausible template with accurate correspondences in an unsupervised manner. Experiments show that our method can not only learn a common implicit template for a collection of shapes, but also establish dense correspondences across all the shapes simultaneously without any supervision.
[arXiv] [Code]
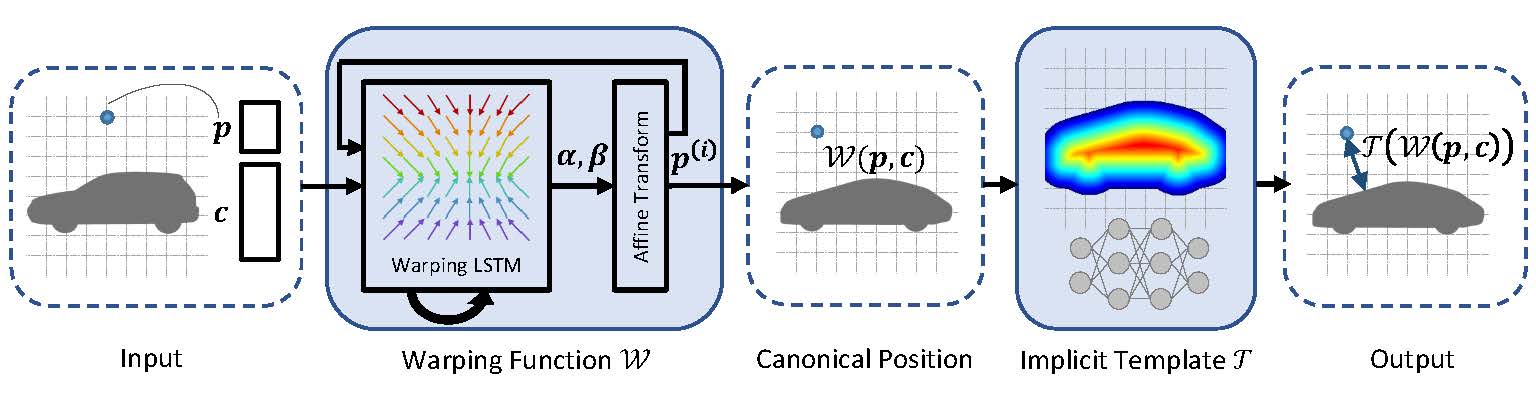
Fig 1. Method overview. Our method decomposes the DIF representation into a warping function and an implicit template. The warping function transforms point samples of a shape instance to their canonical positions, which are then mapped to SDF values by the implicit template.
Results
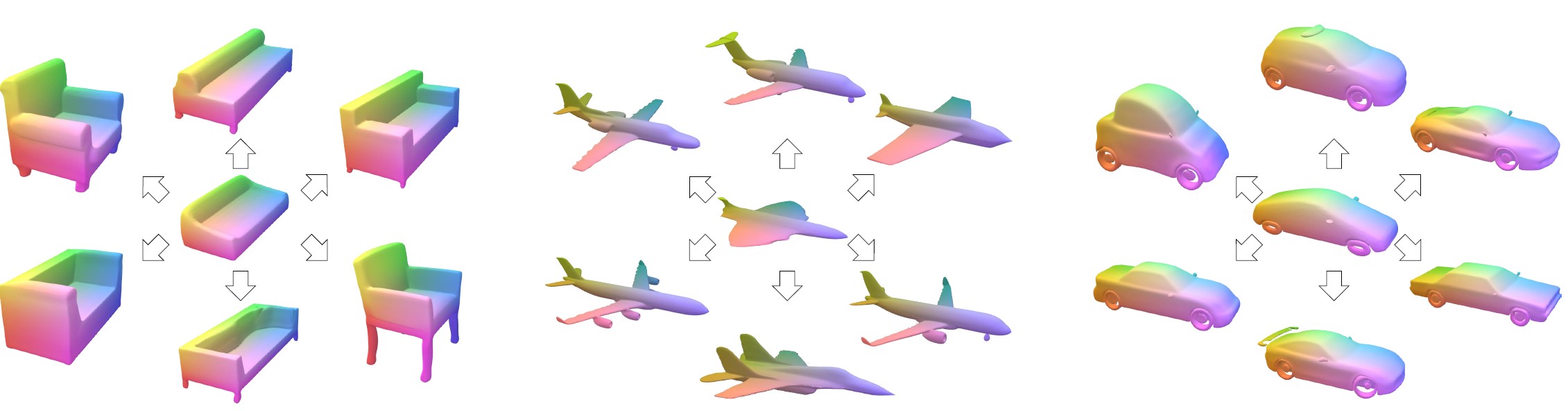
Fig 2. Example results of our representation. Our approach is able to factor out a plausible template (middle) from a set of shapes (surroundings), and builds up dense correspondences (color-coded) across all the shapes automatically without any supervision.
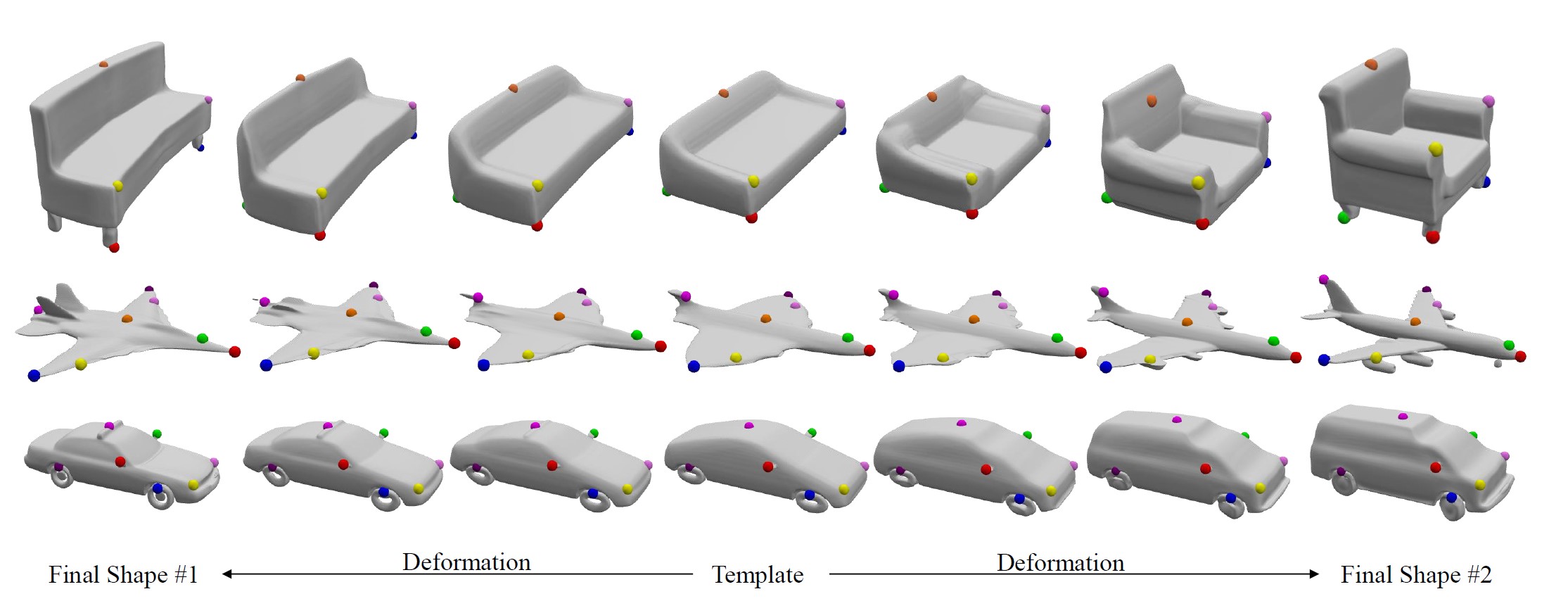
Fig 3. Demonstration of our representation. We manually select several points on the learned templates (middle) and track their traces when the templates deforms to form different shapes (leftmost and rightmost). Note that the deformation is defined and performed in an implicit manner; here we extract the intermediate mesh results for better visualization. The selected points and their movements are rendered as small colored balls.
Technical Paper
[Supplemental Document]
Demo Video
Citation
Zerong Zheng, Tao Yu, Qionghai Dai, Yebin Liu. "Deep Implicit Templates for 3D Shape Representation". arXiv 2020
@InProceedings{zheng2021dit,
title={Deep Implicit Templates for 3D Shape Representation},
author={Zheng, Zerong and Yu, Tao and Dai, Qionghai and Liu, Yebin},
booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (CVPR)},
year={2021},
}
